Snoring is a harsh, loud noise produced from the nose or mouth in sleep due to partial obstruction of the upper airway. Snoring can be an indication that your child may not be getting good quality sleep. Most common cause of snoring in children is adenoid hypertrophy which can happen as a result of repeated viral infections, allergic rhinitis or it may be idiopathic.
Sleep disordered breathing (SDB) is a term used for breathing difficulties during sleep. Chronic nasal blockage in children leads to mouth breathing especially during sleep. Vibrations of the uvula and soft palate in sleep result in snoring.
Lack of good quality sleep in children can lead to hyperactivity, behavioral issues, decreased attention span and poor academic performance. Research shows that children with SDB have cognitive problems especially if they have obstructive sleep apnea.
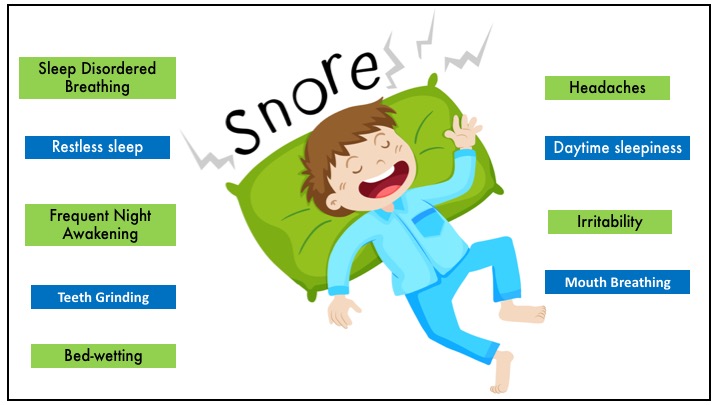
Children who snore more than 3 nights per week are at increased risk of having obstructed sleep apnea which is when a person stops breathing during sleep leading to arousal and poor-quality sleep. Restless sleep, frequent night-time awakenings, teeth grinding and bed-wetting are some of the indicators of SDB. Day-time sleepiness, headaches, increased irritability may also be because of SDB.
Children who snore regularly (10% of the population) require evaluation for the above-mentioned problems. Your doctor might advise you an overnight sleep study that helps in assessing the quality of sleep and detect sleep apneas.